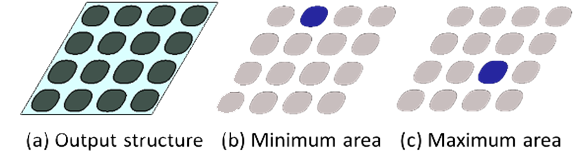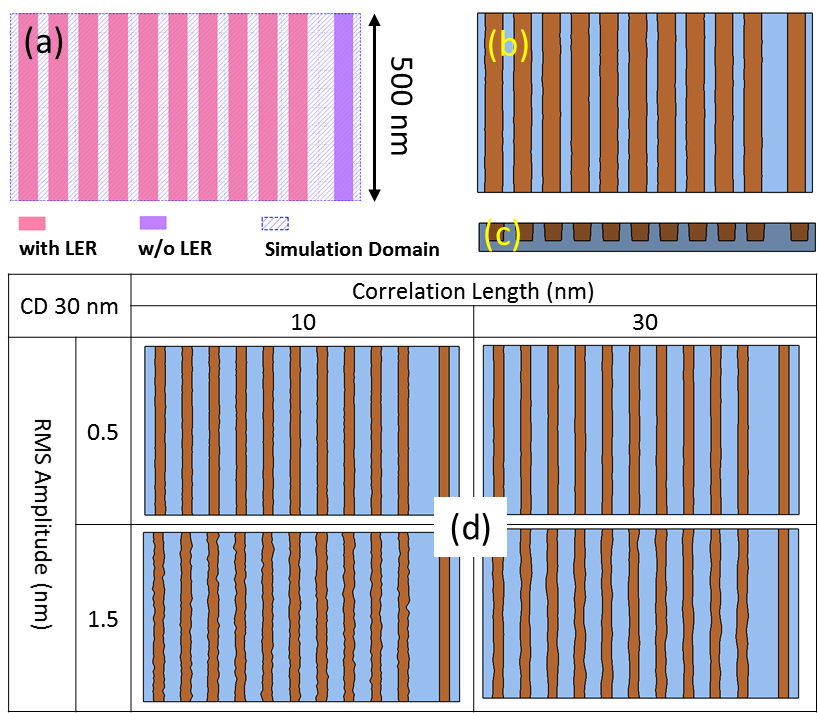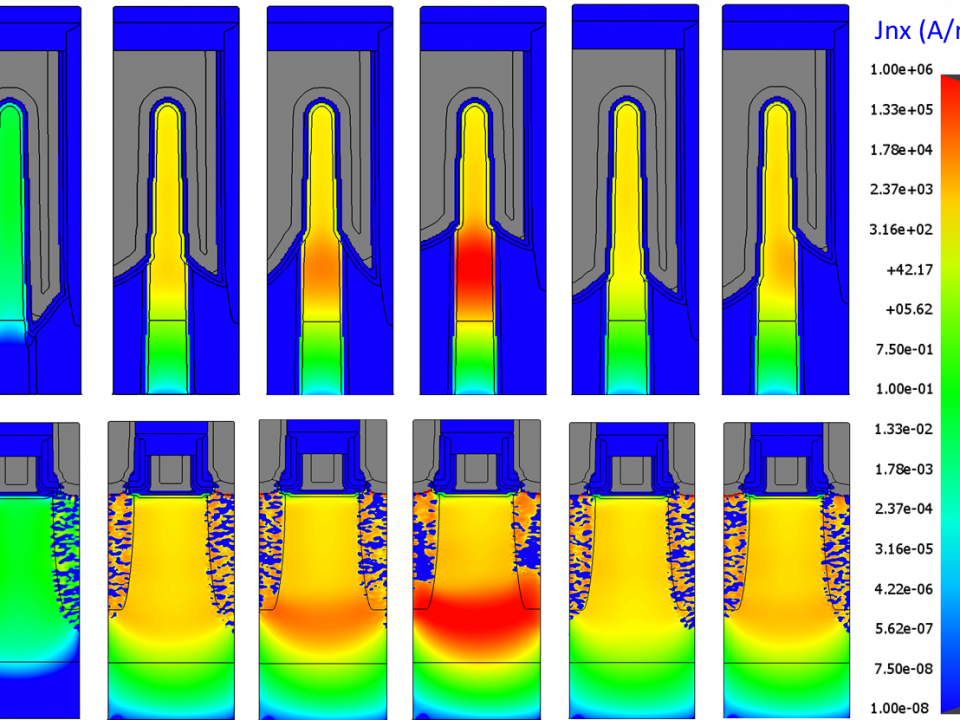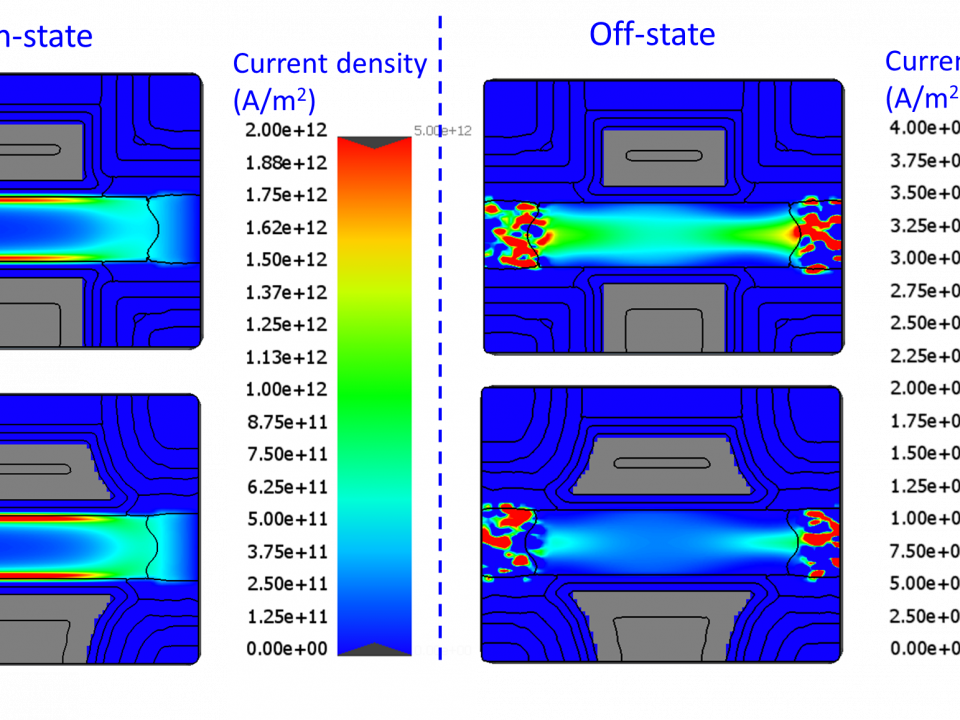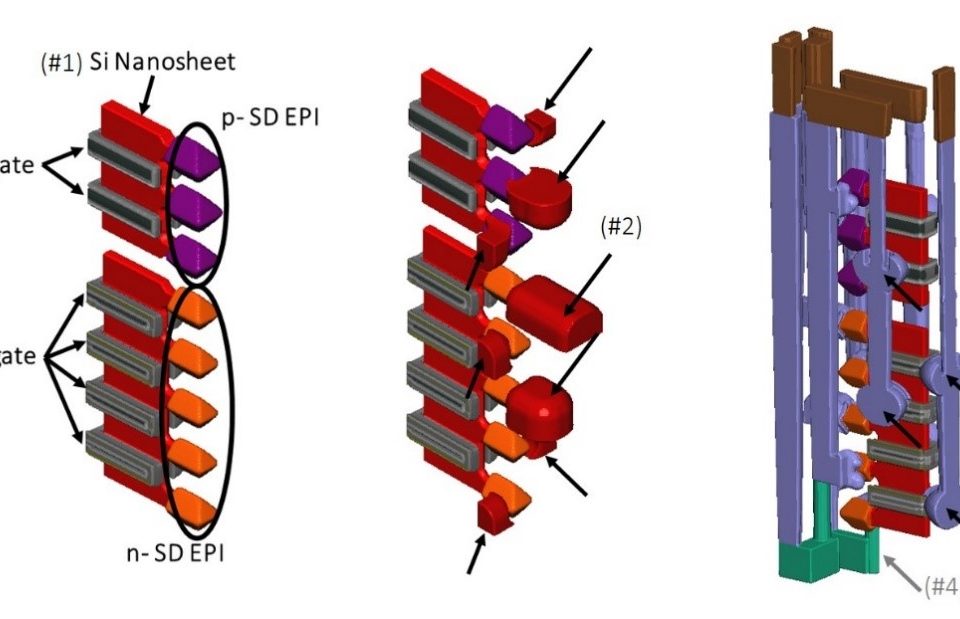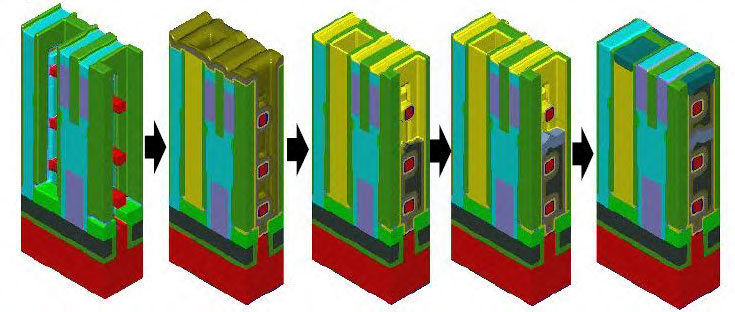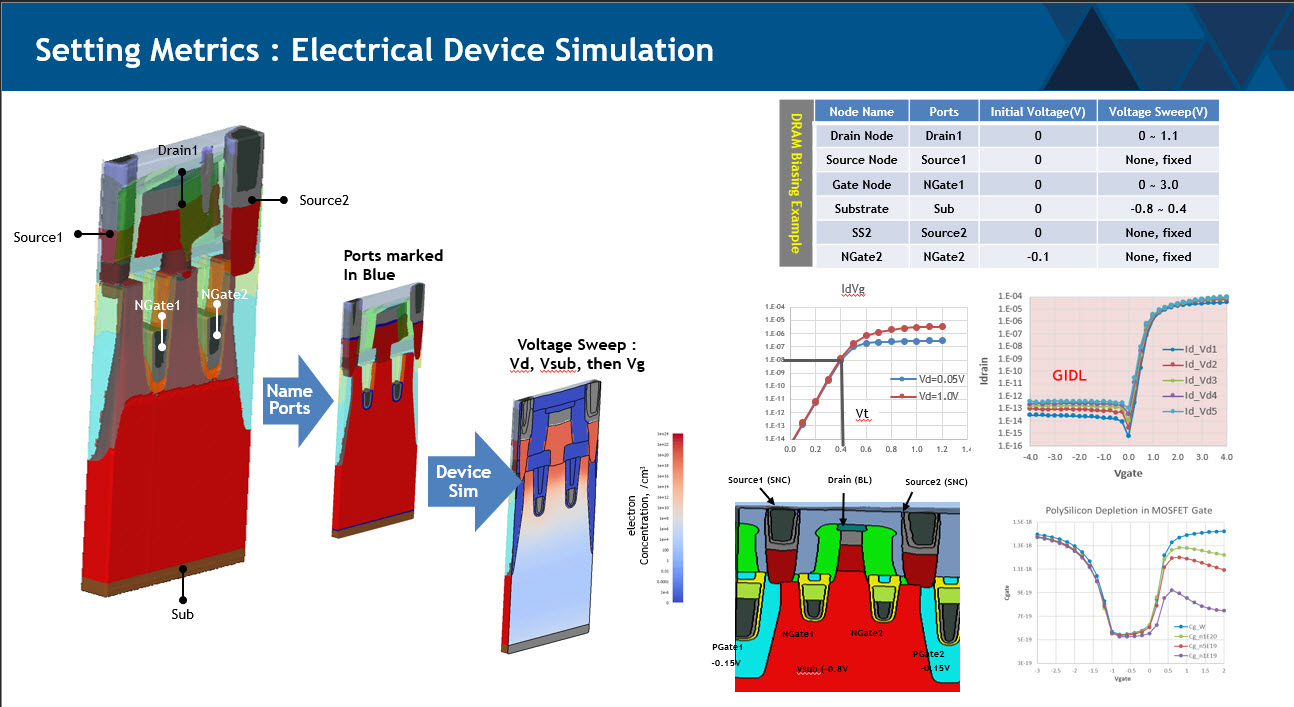
Process Window Optimization of DRAM by Virtual Fabrication
November 24, 2020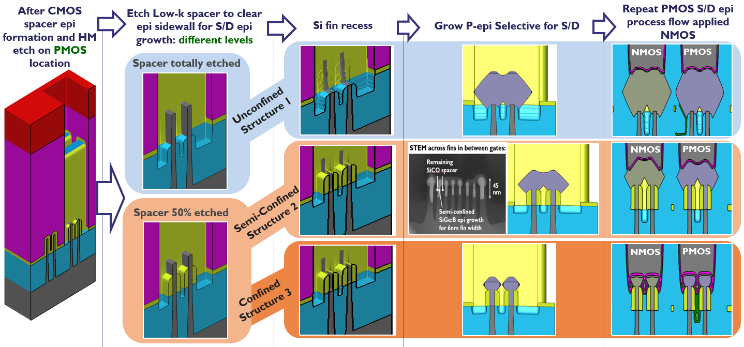
Evaluation of the impact of source drain epi implementation on logic performance using combined process and circuit simulation
December 16, 2020You must have an account on our Customer Portal to access this content. If you already have an account, please log in using the form below or to the right. If you do not have an account, we invite you to request an account.
Whitepaper: Process Variation Analysis of Device Performance Using Virtual Fabrication - Methodology Demonstrated on a CMOS 14-nm FinFET Vehicle
To download your free white paper, please fill out the form below:
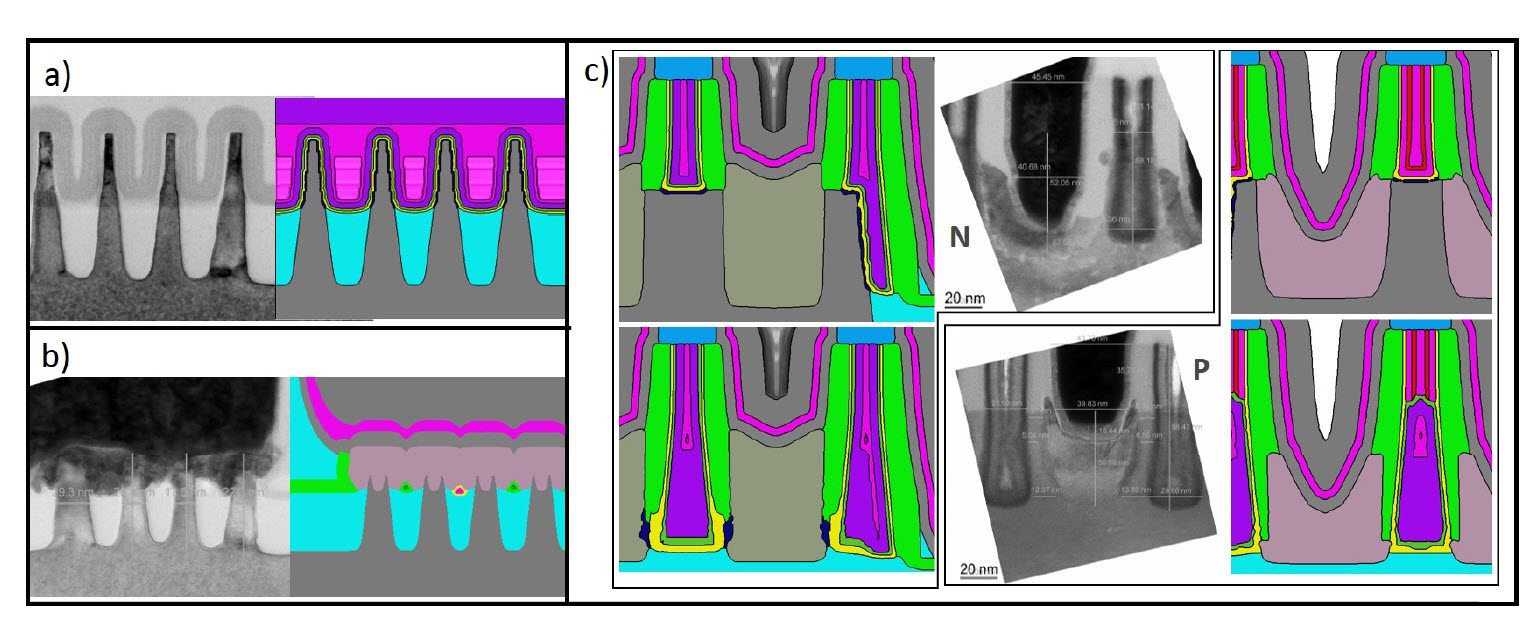
A new methodology is demonstrated to assess the impact of fabrication inherent process variability on 14-nm fin field effect transistor (FinFET) device performance. A model of a FinFET device was built using virtual device fabrication and testing. The model was subsequently calibrated on Design of Experiment corner case data that had been collected on a limited number of processed fab wafers. We then performed 400 virtual experiments comprising seven sources of process variation. Using this virtual fabrication technique, we were able to identify a minimum gate-to-source/drain spacer thickness for a high temperature post-EPI rapid thermal anneal (RTA) anneal process that avoided device subthreshold slope penalties. The model allowed us to determine the optimal Si recess depth target and process window prior to source/drain epitaxy. We obtained these results by reviewing device performance as a function of statistical process sensitivity and highlighting key process parameters requiring variation control. These experiments would have been impractical to perform in an actual fab, due to the time, cost, and equipment requirements of running 400 fab-based process variation experiments for each process parameter. This methodology can be used to avoid wafer-based testing during early technology development.
DOI: 10.1109/TED.2020.3027528
© 2020 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. Permission from IEEE must be obtained for all other uses, in any current or future media, including reprinting/republishing this material for advertising or promotional purposes, creating new collective works, for resale or redistribution to servers or lists, or reuse of any copyrighted component of this work in other works.
You might also be interested in:
- You must have an account on our Customer Portal to access this content. If you already have an account, please log in using the form below or to the right. […]
- You must have an account on our Customer Portal to access this content. If you already have an account, please log in using the form below or to the right. […]
- You must have an account on our Customer Portal to access this content. If you already have an account, please log in using the form below or to the right. […]
- You must have an account on our Customer Portal to access this content. If you already have an account, please log in using the form below or to the right. […]
- You must have an account on our Customer Portal to access this content. If you already have an account, please log in using the form below or to the right. […]
- You must have an account on our Customer Portal to access this content. If you already have an account, please log in using the form below or to the right. […]